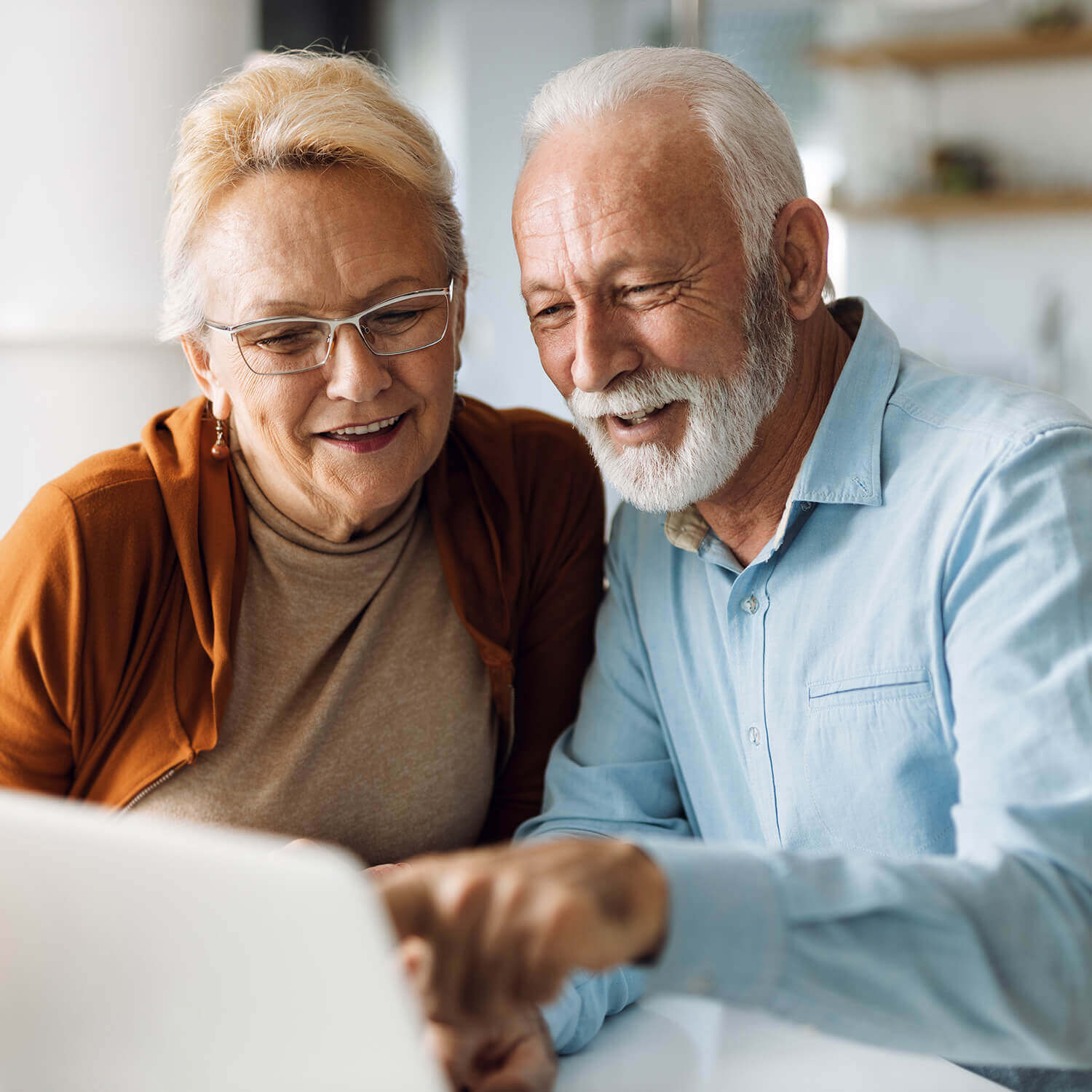

Alzheimer’s Disease Risk DNA Test
$195.00
The Alzheimer’s Disease Risk DNA Test provides insights into your likelihood of developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease by analyzing the APOE gene. Specifically, it looks at the presence of the APOE e4 allele, which is associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s later in life.
- Examines APOE variants (e2, e3, and e4) associated with Alzheimer’s disease risk.
- Simple, at-home sample collection using a painless mouth swab.
- Secure online access to your results, ensuring your privacy.
Summary
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease and the APOE Gene
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory and cognitive functions. As it advances, it can significantly impair daily living and eventually lead to severe mental and physical decline. Although the exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease remain under study, genetics are known to contribute significantly to the risk of developing the condition.
The Apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene is one of the most studied genes in relation to Alzheimer’s disease. This gene is responsible for producing a protein that plays a part in lipid metabolism, including the transportation of cholesterol and other fats in the bloodstream. Importantly, the APOE protein is also involved in neuronal repair, immune response regulation, and the maintenance of synapses in the brain, which are vital for cognitive function.
There are three primary alleles (versions) of the APOE gene: e2, e3, and e4. Everyone has two copies of the APOE gene, one inherited from each parent, and the combination of these alleles can significantly influence an individual’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- e2 Allele: This version is the least common among the three and is associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease. It is believed to offer some protective benefits, potentially due to its role in lipid metabolism and reducing the buildup of amyloid plaques in the brain, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
- e3 Allele: The e3 allele is the most common, present in about half of the population, and is generally considered neutral with respect to Alzheimer’s risk. It neither increases nor decreases the likelihood of developing the disease in a significant way.
- e4 Allele: The e4 allele is associated with a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Individuals carrying one copy of the e4 allele have an increased risk, while those with two copies (e4/e4 genotype) face a significantly higher likelihood of developing the disease, with studies indicating a 10- to 15-fold increased risk compared to those without this allele.
The Alzheimer’s Disease Risk DNA Test
The Alzheimer’s Disease Risk DNA Test is designed to determine which alleles of the APOE gene you carry, offering insights into your genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease. The test is conducted through a non-invasive cheek swab, where your DNA is collected and analyzed to identify the specific APOE alleles present.
- e2/e2 & e2/e3 Genotypes: These combinations are generally associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease. If your test results show one or two copies of the e2 allele, it may indicate a lower chance of developing the condition, although it does not provide absolute immunity.
- e3/e3 Genotype: Individuals with this genotype have a neutral risk, meaning their chances of developing Alzheimer’s disease are similar to the general population.
- e2/e4 & e3/e4 Genotypes: These genotypes suggest an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Those with the e4 allele, particularly the e3/e4 combination, may face about a threefold higher risk compared to those without the e4 allele.
- e4/e4 Genotype: Carrying two copies of the e4 allele indicates a significantly elevated risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, with a 10- to 15-fold increase in likelihood compared to individuals without this allele.
The Alzheimer’s Disease Risk DNA Test offers valuable insights into your genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease by analyzing the APOE gene. By determining whether you carry the e2, e3, or e4 alleles, the test provides a clearer understanding of your potential risk for developing this condition. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and lifestyle, potentially adopting strategies that support brain health and mitigate risk.
How it works

Collect

Ship

Results
Benefits
Convenience
No Hidden Fees
Fast & Accurate
Secure Online Access
About
Why DNA Family Check?
With over 20 years of experience and a proven track record, DNA Family Check is the trusted leader in relationship DNA testing. Our high-volume accredited laboratory has helped millions of families worldwide find answers and resolve questions about their relationships. As pioneers in the industry, we were one of the first to introduce the easy cheek swab method that's now the industry standard.
With our longstanding commitment to excellence and innovation, it's no wonder we're America's #1 choice for paternity answers. Our accredited laboratory is dedicated to providing accurate, reliable, and confidential results, ensuring that families receive the truth they need to move forward. With DNA Family Check, you can trust that you're in good hands.